
| Package | flash.filters |
| Class | public final class GradientBevelFilter |
| Inheritance | GradientBevelFilter  BitmapFilter BitmapFilter  Object Object |
| Language version: | ActionScript 3.0 |
| Runtime version: |
The use of filters depends on the object to which you apply the filter:
filters property. Setting the filters
property of an object does not modify the object, and you can remove the filter by clearing the
filters property. BitmapData.applyFilter() method.
Calling applyFilter() on a BitmapData object takes the source BitmapData object
and the filter object and generates a filtered image as a result.If you apply a filter to a display object, the cacheAsBitmap property of the
display object is set to true. If you clear all filters, the original value of
cacheAsBitmap is restored.
This filter supports Stage scaling. However, it does not support general scaling, rotation,
and skewing; if the object itself is scaled (if scaleX and scaleY are set
to a value other than 1.0), the
filter effect is not scaled. It is scaled only when the user zooms in on the Stage.
A filter is not applied if the resulting image exceeds the maximum dimensions. In AIR 1.5 and Flash Player 10, the maximum is 8,191 pixels in width or height, and the total number of pixels cannot exceed 16,777,215 pixels. (So, if an image is 8,191 pixels wide, it can only be 2,048 pixels high.) In Flash Player 9 and earlier and AIR 1.1 and earlier, the limitation is 2,880 pixels in height and 2,880 pixels in width. For example, if you zoom in on a large movie clip with a filter applied, the filter is turned off if the resulting image exceeds the maximum dimensions.
See also
| Property | Defined by | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| alphas : Array
An array of alpha transparency values for the corresponding colors in the
colors array. | GradientBevelFilter | ||
| angle : Number
The angle, in degrees.
| GradientBevelFilter | ||
| blurX : Number
The amount of horizontal blur.
| GradientBevelFilter | ||
| blurY : Number
The amount of vertical blur.
| GradientBevelFilter | ||
| colors : Array
An array of RGB hexadecimal color values to use in the gradient.
| GradientBevelFilter | ||
 | constructor : Object
A reference to the class object or constructor function for a given object instance.
| Object | |
| distance : Number
The offset distance.
| GradientBevelFilter | ||
| knockout : Boolean
Specifies whether the object has a knockout effect.
| GradientBevelFilter | ||
 | prototype : Object
[static]
A reference to the prototype object of a class or function object.
| Object | |
| quality : int
The number of times to apply the filter.
| GradientBevelFilter | ||
| ratios : Array
An array of color distribution ratios for the corresponding colors in the
colors array. | GradientBevelFilter | ||
| strength : Number
The strength of the imprint or spread.
| GradientBevelFilter | ||
| type : String
The placement of the bevel effect.
| GradientBevelFilter | ||
| Method | Defined by | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
GradientBevelFilter(distance:Number = 4.0, angle:Number = 45, colors:Array = null, alphas:Array = null, ratios:Array = null, blurX:Number = 4.0, blurY:Number = 4.0, strength:Number = 1, quality:int = 1, type:String = "inner", knockout:Boolean = false)
Initializes the filter with the specified parameters.
| GradientBevelFilter | ||
|
Returns a copy of this filter object.
| GradientBevelFilter | ||
 |
Indicates whether an object has a specified property defined.
| Object | |
 |
Indicates whether an instance of the Object class is in the prototype chain of the object specified
as the parameter.
| Object | |
 |
Indicates whether the specified property exists and is enumerable.
| Object | |
 |
Sets the availability of a dynamic property for loop operations.
| Object | |
 |
Returns the string representation of this object, formatted according to locale-specific conventions.
| Object | |
 |
Returns the string representation of the specified object.
| Object | |
 |
Returns the primitive value of the specified object.
| Object | |
| alphas | property |
alphas:Array [read-write]
| Language version: | ActionScript 3.0 |
| Runtime version: |
An array of alpha transparency values for the corresponding colors in the
colors array. Valid values for each element
in the array are 0 to 1. For example, .25 sets a transparency value of 25%.
The alphas property cannot be changed by directly modifying its values.
Instead, you must get a reference to alphas, make the change to the
reference, and then set alphas to the reference.
The colors, alphas, and ratios properties are related.
The first element in the colors array
corresponds to the first element in the alphas array
and in the ratios array, and so on.
public function get alphas():Array
public function set alphas(value:Array):void
TypeError — The Array is null when being set
|
See also
| angle | property |
angle:Number [read-write]
| Language version: | ActionScript 3.0 |
| Runtime version: |
The angle, in degrees. Valid values are 0 to 360. The default is 45.
The angle value represents the angle of the theoretical light source falling on the object. The value determines the angle at which the gradient colors are applied to the object: where the highlight and the shadow appear, or where the first color in the array appears. The colors are then applied in the order in which they appear in the array.
Implementation public function get angle():Number
public function set angle(value:Number):void
See also
| blurX | property |
blurX:Number [read-write]
| Language version: | ActionScript 3.0 |
| Runtime version: |
The amount of horizontal blur. Valid values are 0 to 255. A blur of 1 or less means that the original image is copied as is. The default value is 4. Values that are a power of 2 (such as 2, 4, 8, 16 and 32) are optimized to render more quickly than other values.
Implementation public function get blurX():Number
public function set blurX(value:Number):void
| blurY | property |
blurY:Number [read-write]
| Language version: | ActionScript 3.0 |
| Runtime version: |
The amount of vertical blur. Valid values are 0 to 255. A blur of 1 or less means that the original image is copied as is. The default value is 4. Values that are a power of 2 (such as 2, 4, 8, 16 and 32) are optimized to render more quickly than other values.
Implementation public function get blurY():Number
public function set blurY(value:Number):void
| colors | property |
colors:Array [read-write]
| Language version: | ActionScript 3.0 |
| Runtime version: |
An array of RGB hexadecimal color values to use in the gradient. For example, red is 0xFF0000, blue is 0x0000FF, and so on.
The colors property cannot be changed by directly modifying its values.
Instead, you must get a reference to colors, make the change to the
reference, and then set colors to the reference.
The colors, alphas, and ratios properties are related.
The first element in the colors array
corresponds to the first element in the alphas array
and in the ratios array, and so on.
public function get colors():Array
public function set colors(value:Array):void
TypeError — The Array is null when being set
|
See also
| distance | property |
distance:Number [read-write]
| Language version: | ActionScript 3.0 |
| Runtime version: |
The offset distance. Valid values are 0 to 8. The default value is 4.0.
Implementation public function get distance():Number
public function set distance(value:Number):void
| knockout | property |
knockout:Boolean [read-write]
| Language version: | ActionScript 3.0 |
| Runtime version: |
Specifies whether the object has a knockout effect. A knockout effect
makes the object's fill transparent and reveals the background color of the document.
The value true specifies a knockout effect;
the default is false (no knockout effect).
public function get knockout():Boolean
public function set knockout(value:Boolean):void
| quality | property |
quality:int [read-write]
| Language version: | ActionScript 3.0 |
| Runtime version: |
The number of times to apply the filter. The default value is BitmapFilterQuality.LOW,
which is equivalent to applying the filter once. The value BitmapFilterQuality.MEDIUM
applies the filter twice; the value BitmapFilterQuality.HIGH applies it three times.
Filters with lower values are rendered more quickly.
For most applications, a quality value of low, medium, or high is sufficient.
Although you can use additional numeric values up to 15 to achieve different effects,
higher values are rendered more slowly. Instead of increasing the value of quality,
you can often get a similar effect, and with faster rendering, by simply increasing the values
of the blurX and blurY properties.
public function get quality():int
public function set quality(value:int):void
See also
| ratios | property |
ratios:Array [read-write]
| Language version: | ActionScript 3.0 |
| Runtime version: |
An array of color distribution ratios for the corresponding colors in the
colors array. Valid values for each element
in the array are 0 to 255.
The ratios property cannot be changed by directly modifying its values.
Instead, you must get a reference to ratios, make the change to the
reference, and then set ratios to the reference.
The colors, alphas, and ratios properties are related.
The first element in the colors array
corresponds to the first element in the alphas array
and in the ratios array, and so on.
To understand how the colors in a gradient bevel are distributed, think first of the colors that you want in your gradient bevel. Consider that a simple bevel has a highlight color and shadow color; a gradient bevel has a highlight gradient and a shadow gradient. Assume that the highlight appears on the top-left corner, and the shadow appears on the bottom-right corner. Assume that one possible usage of the filter has four colors in the highlight and four in the shadow. In addition to the highlight and shadow, the filter uses a base fill color that appears where the edges of the highlight and shadow meet. Therefore the total number of colors is nine, and the corresponding number of elements in the ratios array is nine.
If you think of a gradient as composed of stripes of various colors, blending into each other, each ratio value sets the position of the color on the radius of the gradient, where 0 represents the outermost point of the gradient and 255 represents the innermost point of the gradient. For a typical usage, the middle value is 128, and that is the base fill value. To get the bevel effect shown in the image below, assign the ratio values as follows, using the example of nine colors:
If you want an equal distribution of colors for each edge, use an odd number of colors, where the middle color is the base fill. Distribute the values between 0-127 and 129-255 equally among your colors, then adjust the value to change the width of each stripe of color in the gradient. For a gradient bevel with nine colors, a possible array is [16, 32, 64, 96, 128, 160, 192, 224, 235]. The following image depicts the gradient bevel as described:
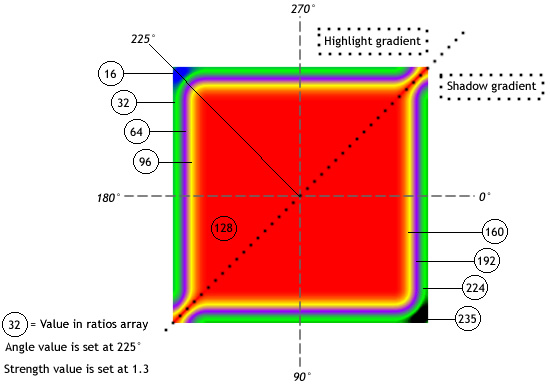
Keep in mind that the spread of the colors in the gradient varies based on the values
of the blurX, blurY, strength, and quality
properties, as well as the ratios values.
public function get ratios():Array
public function set ratios(value:Array):void
TypeError — The Array is null when being set
|
See also
| strength | property |
strength:Number [read-write]
| Language version: | ActionScript 3.0 |
| Runtime version: |
The strength of the imprint or spread. The higher the value, the more color is imprinted and the stronger the contrast between the bevel and the background. Valid values are 0 to 255. A value of 0 means that the filter is not applied. The default value is 1.
Implementation public function get strength():Number
public function set strength(value:Number):void
See also
| type | property |
type:String [read-write]
| Language version: | ActionScript 3.0 |
| Runtime version: |
The placement of the bevel effect. Possible values are BitmapFilterType constants:
BitmapFilterType.OUTER — Bevel on the outer edge of the objectBitmapFilterType.INNER — Bevel on the inner edge of the objectBitmapFilterType.FULL — Bevel on top of the object public function get type():String
public function set type(value:String):void
| GradientBevelFilter | () | constructor |
public function GradientBevelFilter(distance:Number = 4.0, angle:Number = 45, colors:Array = null, alphas:Array = null, ratios:Array = null, blurX:Number = 4.0, blurY:Number = 4.0, strength:Number = 1, quality:int = 1, type:String = "inner", knockout:Boolean = false)
| Language version: | ActionScript 3.0 |
| Runtime version: |
Initializes the filter with the specified parameters.
Parametersdistance:Number (default = 4.0) |
|
angle:Number (default = 45) |
|
colors:Array (default = null) |
|
alphas:Array (default = null)colors array. Valid values for each element in the array are 0 to 1.
For example, .25 sets a transparency value of 25%.
|
|
ratios:Array (default = null) |
|
blurX:Number (default = 4.0) |
|
blurY:Number (default = 4.0) |
|
strength:Number (default = 1) |
|
quality:int (default = 1)
For more information, see the description of the |
|
type:String (default = "inner")
|
|
knockout:Boolean (default = false)true
makes the object's fill transparent and reveals the background color of the document.
|
See also
| clone | () | method |
public override function clone():BitmapFilter
| Language version: | ActionScript 3.0 |
| Runtime version: |
Returns a copy of this filter object.
ReturnsBitmapFilter —
A new GradientBevelFilter instance with all the
same properties as the original GradientBevelFilter instance.
|
draw() method, which uses methods of the Graphics class
accessed through the graphics property of Sprite to draw a gray square.filter and assigns it
the return value of a call to getBitmapFilter(), which creates the filter.myFilters and adds filter to it.myFilters to the filters property of the
GradientBevelFilterExample object. This applies all filters found in myFilters, which in this case
is only filter.
package {
import flash.display.Sprite;
import flash.filters.BitmapFilter;
import flash.filters.BitmapFilterQuality;
import flash.filters.BitmapFilterType;
import flash.filters.GradientBevelFilter;
public class GradientBevelFilterExample extends Sprite {
private var bgColor:uint = 0xCCCCCC;
private var size:uint = 80;
private var offset:uint = 50;
private var distance:Number = 5;
private var angleInDegrees:Number = 225; // opposite 45 degrees
private var colors:Array = [0xFFFFFF, 0xCCCCCC, 0x000000];
private var alphas:Array = [1, 0, 1];
private var ratios:Array = [0, 128, 255];
private var blurX:Number = 8;
private var blurY:Number = 8;
private var strength:Number = 2;
private var quality:Number = BitmapFilterQuality.HIGH
private var type:String = BitmapFilterType.INNER;
private var knockout:Boolean = true;
public function GradientBevelFilterExample() {
draw();
var filter:BitmapFilter = getBitmapFilter();
var myFilters:Array = new Array();
myFilters.push(filter);
filters = myFilters;
}
private function getBitmapFilter():BitmapFilter {
return new GradientBevelFilter(distance,
angleInDegrees,
colors,
alphas,
ratios,
blurX,
blurY,
strength,
quality,
type,
knockout);
}
private function draw():void {
graphics.beginFill(bgColor);
graphics.drawRect(offset, offset, size, size);
graphics.endFill();
}
}
}
